Ceramic implants are one of the relatively newer and most exciting developments in oral implantology. These implants have been used in Europe since the early 2000s and, subsequent to FDA approval in 2011, in the United States. The first ceramic material that was used in the past for dental implants was aluminum oxide. This material showed good osseointegration, but it did not have adequate mechanical properties for long-term loading. More recently, a new generation of ceramic materials, such as zirconia (ZrO2), was introduced.
Category Archives: All
“Due to NIH’s all-hands-on-deck response to the pandemic, researchers at the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research were able to quickly pivot and apply their expertise in oral biology and medicine to answering key questions about COVID-19,” said NIDCR Director Rena D’Souza, D.D.S., M.S., Ph.D. “The power of this approach is exemplified by the efforts of this scientific team, who identified a likely role for the mouth in SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission, a finding that adds to knowledge critical for combatting this disease.”
BADALONA, Spain: Mouthwashes that contain cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) have been found to reduce by at least one thousand times the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Researchers in Spain tested CPC-containing mouthwashes against variants of SARS-CoV-2, including the Alpha variant, and said that such mouth rinses could constitute a cost-effective measure to aid in the reduction of viral transmission.
Older adults with more harmful than healthy bacteria in their gums are more likely to have evidence for amyloid beta — a key biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease — in their cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), according to new research from NYU College of Dentistry and Weill Cornell Medicine. However, this imbalance in oral bacteria was not associated […]
Current advice from the America Dental Association tells you that if your gums bleed, make sure you are brushing and flossing twice a day because it could be a sign of gingivitis, an early stage of periodontal disease. And that might be true. So if you are concerned, see your dentist. However, a new University of Washington study suggests you should also check your intake of vitamin C.
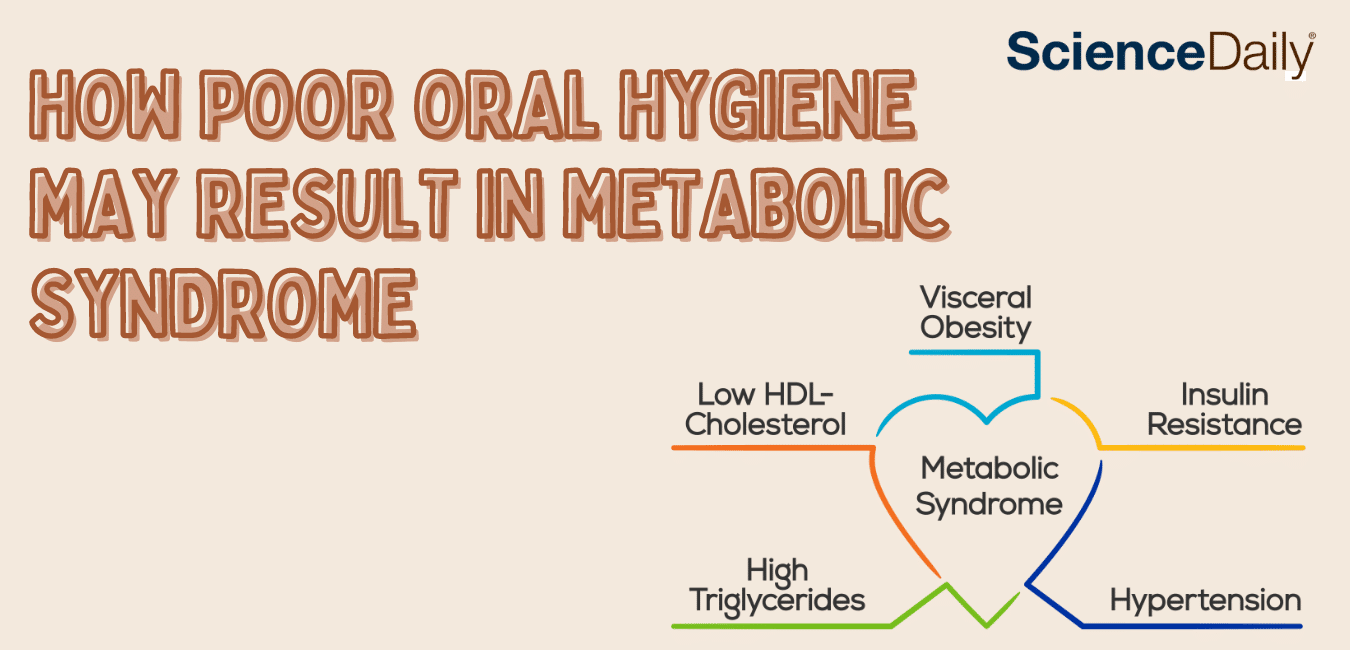
Periodontal or gum disease is known to be a significant risk factor of metabolic syndrome, a group of conditions increasing the risk for heart disease and diabetes. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered that infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis, the bacterium causing periodontal disease, causes skeletal muscle metabolic dysfunction, the precursor to metabolic syndrome, by altering the composition of the gut microbiome.
Periodontitis is associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease, and the risk increases for those with more severe gum disease, according to research being presented this week at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) virtual meeting.
Obesity is associated with worse periodontal conditions, according to a recent literature review on the relationship between obesity and periodontal disease. Conversely, periodontal treatment appears to significantly reduce several biochemical biomarkers associated with obesity.
COVID-19 could pass into people’s lungs from saliva with the virus moving directly from mouth to bloodstream – particularly if individuals are suffering from gum disease, according to new research.
SARS-CoV-2 spreads mainly through respiratory droplets, and dental procedures are known to produce an abundance of aerosols — leading to fears that flying saliva during a cleaning or a restorative procedure could make the dentist’s chair a high-transmission location.